The vagus nerve
Interface between brain and body
Interface between brain and body
In this article, we look at the function of the vagus nerve, which plays a key role in the parasympathetic nervous system, considered the body’s ‘rest and digest’ system. From regulating heart rate to improving resilience, find out how the vagus nerve affects your health and what medical innovations are promising in this area.
The vagus nerve is one of the most important nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is often referred to as the body’s “rest and digest” system. The function and importance of the vagus nerve and the parasympathetic nervous system have already been explained in detail in a previous article. To understand this article, it is sufficient to know that the vagus nerve plays a key role in the regulation of various bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion and inflammatory responses.
The vagus nerve acts as a kind of “communication highway” between the brain and important organs such as the heart, lungs and intestines. It transmits signals in both directions, enabling the fine-tuning and coordination of various physiological processes.
Interestingly, recent studies indicate that high vagal activity is associated with better emotional and psychological resilience. The ability to recover quickly from stressors is often more pronounced in people with high vagus activity.
The vagus nerve has a direct influence on the heart rate and is of crucial importance for the fine-tuning of the heartbeat. It sends parasympathetic signals to the heart, which have a slowing effect in contrast to the sympathetic signals that accelerate the heartbeat. By releasing neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, the vagus nerve brings about a reduction in the heart rate and thus contributes to a calmer and more even heartbeat.
Without regulation by the vagus nerve, the heart would beat normally. This is because the sympathetic nervous system, the other part of the autonomic nervous system, tends to increase the heart rate. The vagus nerve acts as a kind of counterbalance here and ensures a balance between speeding up and slowing down the heartbeat.
In a state without vagus activity, the heartbeat can be irregular and accelerated, which can increase the risk of various cardiovascular diseases. Fine-tuning by the vagus nerve is therefore of paramount importance for maintaining healthy heart function.
The role of the vagus nerve in regulating heart rate has been the subject of numerous scientific studies in animals and humans. A common method for studying the effects of the vagus nerve on heart rate is vagotomy, a surgical procedure in which the vagus nerve is severed or partially removed. By removing the vagus nerve, it is possible to measure the “internal” or “intrinsic” heart rate of the heart, which is significantly higher than the heart rate under normal conditions when the vagus nerve is active.
Pharmacological methods, in which the vagus nerve is blocked by medication, also provide similar results. In both cases, it is observed that the heart rate increases when the activity of the vagus nerve is inhibited or switched off.
In addition, electrophysiological studies provide further insight into the mechanisms by which the vagus nerve influences heart rate. These studies have shown that the vagus nerve plays a key role in lowering the heart rate and that the heart would beat faster without its influence.
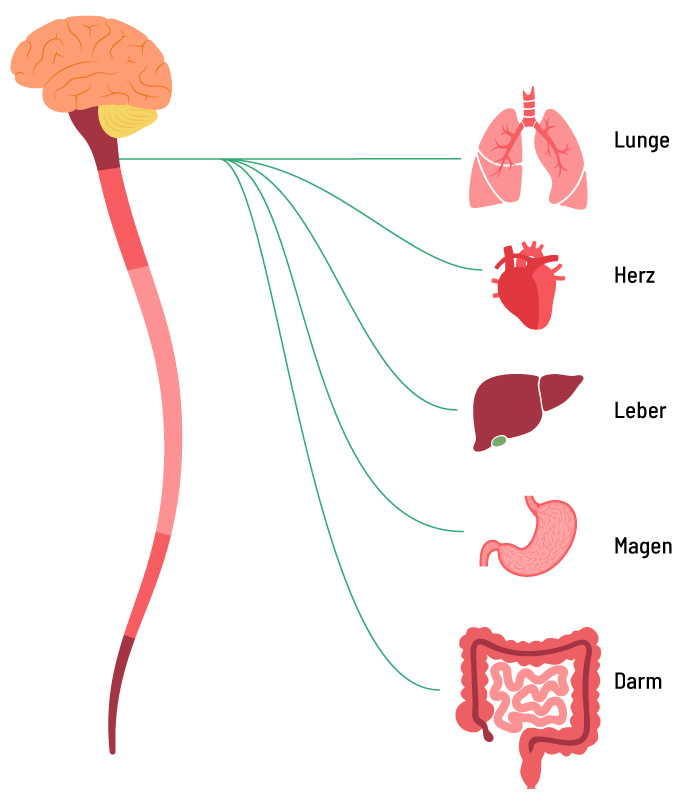
As part of the parasympathetic nervous system, the vagus nerve supplies vital organs
A vagus pacemaker is sometimes used to treat various diseases in order to stimulate the activity of the vagus nerve.
X-ray image of an implanted vagus nerve stimulator
Image source: Hellerhoff, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Vagus nerve stimulation can reduce the frequency and severity of epileptic seizures. It is often an option for patients for whom medication is not effective or has undesirable side effects.
Early studies show that vagus nerve stimulation could be a promising treatment option for difficult-to-treat forms of depression. As the vagus nerve plays a role in regulating mood and stress responses, it is thought that its stimulation could have positive effects.
In inflammatory diseases such as chronic arthritis, stimulation of the vagus nerve can help to reduce inflammation. This is because the vagus nerve is involved in the regulation of the immune system.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve can also help to prevent migraine attacks. The transmission of stimuli to the brain leads to the stimulation of brain regions that are affected in pain and migraine patients
The vagus nerve plays an important role in pain. Stimulation of the vagus nerve with weak electrical impulses can help to alleviate even chronic pain that has not yet been treated
With ongoing research and the development of new technologies, vagus nerve stimulation could find an even wider range of applications in the future. However, patients and doctors should carefully consider the risks and alternatives. Although the therapy is promising, there are also some concerns and alternatives that should be considered.
A vagus nerve pacemaker requires a surgical procedure that is associated with risks, including infection or problems with device placement.
Side effects may include hoarseness, difficulty breathing and difficulty swallowing. Although these are usually mild, they should be taken into account.
The high cost of the equipment and surgery can be a barrier, especially in countries without comprehensive healthcare.
In many cases, non-invasive methods such as transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (t-VNS) may be a less risky option. Also, conventional treatment methods such as medication or behavioral therapy are often the first choice before resorting to more invasive methods.
FaceFormer therapy can support the function of the vagus nerve and thus strengthen the entire nervous system. By specifically training the muscles and movement patterns of the mouth and throat and through targeted breathing exercises, FaceFormer therapy can do much to reduce stress, alleviate digestive problems, improve breathing and promote the general ability to relax. Possible surgical risks are excluded from the outset with non-invasive procedures such as FaceFormer therapy.
The vagus nerve plays an important role in the release of acetylcholine, one of the main neurotransmitters responsible for communication between nerve and muscle cells. Acetylcholine acts as a signaling agent that helps to lower the heart rate and aid digestion, among other functions. Acetylcholine is also involved in various forms of brain communication, and its release through the vagus nerve has effects on mood, immune response and inflammatory reactions.
Insufficient vagus nerve activity can lead to a reduction in the release of acetylcholine, which in turn can cause a number of problems. These can include an increased heart rate, problems with digestion and possibly an increased inflammatory response. Low vagal activity has also been linked to conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression and chronic inflammatory conditions. In such cases, vagus nerve stimulation may be considered as a treatment option to modulate neurotransmitter activity and alleviate symptoms.
The role of neurotransmitters in signal transmission between neurons is an essential part of our understanding of neuronal function. Their existence was first postulated at the beginning of the 20th century. Pioneers such as Otto Loewi and Henry Dale carried out crucial experiments that eventually led to the identification of acetylcholine as one of the first neurotransmitters. Loewi and Dale were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1936 for their discoveries in the chemical transmission of nerve impulses.
Breathing is of crucial importance in regulating the activity of the vagus nerve and can be used to specifically modulate the effects of the parasympathetic nervous system on the body.
The vagus nerve plays a central role in the regulation of breathing. It is not only involved in controlling the bronchial muscles, but also in transmitting signals from the lungs to the brain. The vagus nerve helps to monitor the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood and adjust them accordingly. This function is essential for maintaining homeostasis and general well-being.
The type of breathing can also have an effect on vagal activity. Nasal breathing is considered more beneficial as it filters, humidifies and warms the air before it reaches the lungs. It also allows for deeper, slower breathing, which can stimulate vagus nerve activity. Mouth breathing, on the other hand, can lead to less effective oxygenation and less stimulation of the vagus nerve.
Mouth breathing activates the sympathetic nervous system, which can lead to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This can lead to increased stress levels and increased tension in the body. Nasal breathing, on the other hand, activates the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for relaxation and regeneration. Nasal breathing can therefore help to calm the body and reduce stress.
Various breathing techniques, especially those that prolong the exhalation phase, can increase the activity of the vagus nerve and thus the parasympathetic nervous system. This often leads to deeper relaxation and a reduction in the heart rate. Breathing exercises aimed at activating the vagus nerve are sometimes used in the treatment of anxiety, depression and stress.
The pharynx is a complex region of the body in which various nerve tracts and muscles interact, including the vagus nerve and the glossopharyngeal nerve. The vagus nerve plays a key role in controlling the muscles in the pharynx and plays an important role in swallowing movements, regulating vocal pitch and breathing. Due to its proximity to the glossopharyngeus, there is a close anatomical and functional connection, which is particularly evident in coordinated movements such as swallowing.
The swallowing function is a highly complex activity that requires precise coordination between different nerves and muscles. Both the vagus nerve and the glossopharyngeal nerve are involved in this coordination. They help to control the muscles that move the bolus of food from the mouth to the stomach. A lack of coordination or stimulation by one of these nerves can lead to swallowing disorders, which can have serious health consequences such as aspiration pneumonia or malnutrition.
The close connection between the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves in the pharynx is therefore not only important for basic functions such as swallowing and breathing, but also for monitoring and regulating many other vital processes.
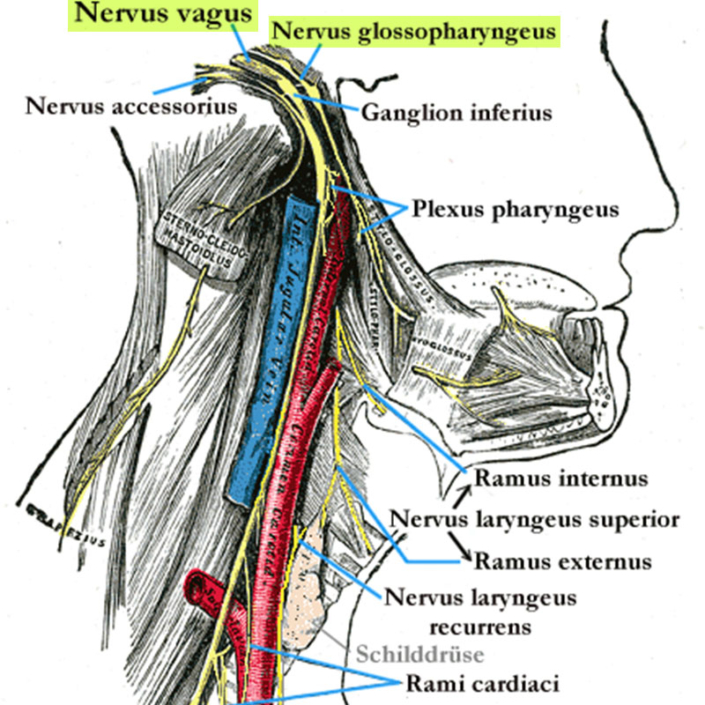
Course of the glossopharyngeal nerve in relation to the vagus nerve
Image source: de:Benutzer:Uwe Gille, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The right breathing technique plays a crucial role in activating the vagus nerve. Conscious, deep abdominal breathing can stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system and thus reduce stress and tension. Breathing therefore not only serves to supply oxygen, but also has a significant influence on neurological and psychological well-being.

There are various ways to positively activate the vagus nerve and thereby promote the function of the parasympathetic nervous system. Some of these methods are
Targeted FaceFormer exercises improve nasal breathing and activate the parasympathetic nervous system by stimulating the vagus nerve.
Techniques that focus on breathing in particular can stimulate the activity of the vagus nerve.
Certain yoga poses and breathing techniques are designed to activate the parasympathetic nervous system and thus the vagus nerve.
Cold water applications or cold stimuli can stimulate the vagus nerve and thus lower the heart rate and blood pressure.
Moderate exercise can promote vagal activity, while too intense sport tends to activate the sympathetic nervous system.
Certain nutrients and probiotic bacteria can positively influence the activity of the vagus nerve.
In the complex world of the human nervous system, the vagus nerve plays a crucial role in regulating numerous bodily functions. Understanding the functions of this nerve reveals new ways to treat a wide range of conditions, from heart problems to mental disorders. It is always important to carefully weigh up the risks and alternatives. FaceFormer training and targeted breathing exercises can offer promising treatment alternatives alongside technically invasive methods such as the use of so-called vagus pacemakers.
You can purchase your FaceFormer online in the Dr. Berndsen Shop, from our sales partners or from numerous doctors and therapists or locally in your pharmacy.
Ask for the central pharmaceutical number PZN 18092273 (FaceFormer ONE blue).
Further product variants and useful accessories are available.
Saving tip especially for doctors and therapists: 20%++ discount on orders of 5 FaceFormers or more!
The effective solution for snoring, sleep apnea, CMD, jaw problems and many other indications. Simple, causal, effective.
Wasserstr.25
59423 Unna
Germany
+49 (0) 23 03-89 99 1
+49 (0) 23 03 – 89 88 6
Mo. to Fr. from 8:00 to 16:00

This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
OK, agree with allAgree to essentialsShow settingsThe satisfaction of visitors to our website is important to us. In order to better address you, we use cookies. Thereby we achieve that the website works technically reliable and secure.
You can change or revoke your consent at any time.
In the privacy policy you can learn more about cookies and privacy setting.
View privacy policy
Essential cookies enable basic functionality and are necessary for the proper functioning of the website.
This data may be linked to user information of users logged in on youtube.com and google.com.
YouTube video embedding
Used to unlock YouTube content.
Google Analytics
Cookie from Google for website analytics.
Generates statistical data about how the visitor uses the website
